








Form in the textile art, as in all other useful arts, is fundamentally, although not exclusively, the resultant or expression of function, but at the same time it is further than in other shaping arts from expressing the whole of function. Such is the pliability of a large portion of textile products—as, for example, nets, garments, and hangings—that the shapes assumed are variable, and, therefore, when not distended or for some purpose folded or draped, the articles are without esthetic value or interest. The more rigid objects, in common with the individuals of other useful arts, while their shape still accords with their functional office, exhibit attributes of form generally recognized as pleasing to the mind, which are expressed by the terms grace, elegance, symmetry, and the like. Such attributes are not separable from functional attributes, but originate and exist conjointly with them.
In addition to these features of form we observe others of a more decidedly superfunctional character, added manifestly for the purpose of enhancing the appearance.
In very primitive times when a utensil is produced functional ideas predominate, and there is, perhaps, so far as its artificial characters are concerned, a minimum of comeliness. But as the ages pass by essential features are refined and elements of beauty are added and emphasized. In riper culture the growing pressure of esthetic desire leads to the addition of many superficial modifications whose chief office is to please the fancy. In periods of deadened sensibility or even through the incompetence of individual artists in any period, such features may be ill chosen and erroneously applied, interfering with construction and use, and thus violating well founded and generally accepted canons of taste. In respect to primitive works we may distinguish four steps in the acquisition of esthetic features of form, three of which are normal, the fourth abnormal: First, we have that in which functional characters alone are considered, any element of beauty, whether due to the artist's hand or to the accidents of material, construction, or model, being purely adventitious; second, that in which the necessary features of the utensil appear to have experienced the supervision of taste, edges being rounded, curves refined, and symmetry perfected; third, that in which the functionally perfect object, just described, undergoes further variations of contour, adding to variety, unity, &c., thus enhancing beauty without interfering with serviceability; and, fourth, that in which, under abnormal influences, beauty is sought at the sacrifice of functional and constructive perfection.
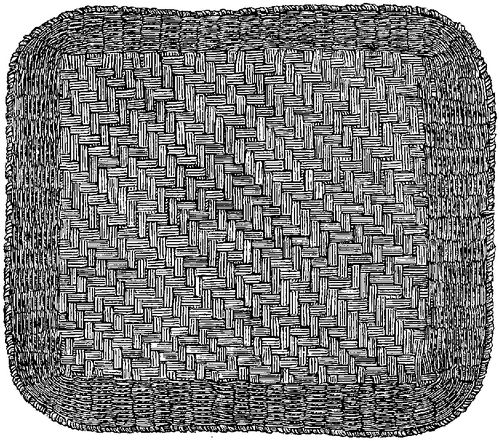
Fig. 286. Mat or tray exhibiting a minimum of esthetic attributes of form. Moki work—1/8.ToList
The exact relations of the various classes of forces and phenomena pertaining to this theme may be more fully elucidated by the aid of illustrations. Woven mats, in early use by many tribes of men and originating in the attempt to combine leaves, vines, and branches for purposes of comfort, are flat because of function, the degree of flatness depending upon the size of filaments and mode of combination; and in outline they are irregular, square, round, or oval, as a result of many causes and influences, embracing use, construction, material, models, &c. A close approach to symmetry, where not imposed by some of the above mentioned agencies, is probably due to esthetic tendencies on the part of the artist. The esthetic interest attaching to such a shape cannot be great, unless perhaps it be regarded, as all individuals and classes may be regarded, in its possible relations to preceding, associated, and succeeding forms of art. The varied features observed upon the surface, the colors and patterns (Fig. 286), pertain to design rather than to form and will receive attention in the proper place.
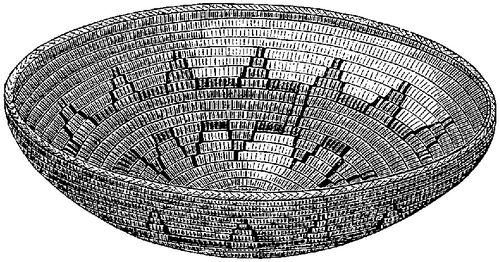
Fig. 287. Tray having decided esthetic attributes of form. Obtained from the Apache—1/2.ToList
In point of contour the basket tray shown in Fig. 287 has a somewhat more decided claim upon esthetic attention than the preceding, as the curves exhibited mark a step of progress in complexity and grace. How much of this is due to intention and how much to technical perfection must remain in doubt. In work so perfect we are wont, however unwarrantably, to recognize the influence of taste.

Fig. 288. Pyriform water vessel used by the Piute Indians—1/8.ToList
A third example—presented in Fig. 288—illustrates an advanced stage in the art of basketry and exhibits a highly specialized shape. The forces and influences concerned in its evolution may be analyzed as follows: A primal origin in function and a final adaptation to a special function, the carrying and storing of water; a contour full to give capacity, narrow above for safety, and pointed below that it may be set in sand; curves kept within certain bounds by the limitations of construction; and a goodly share of variety, symmetry, and grace, the result to a certain undetermined extent of the esthetic tendencies of the artist's mind. In regard to the last point there is generally in forms so simple an element of uncertainty; but many examples may be found in which there is positive evidence of the existence of a strong desire on the part of the primitive basketmaker to enhance beauty of form. It will be observed that the textile materials and construction do not lend themselves freely to minuteness in detail or to complexity of outline, especially in those small ways in which beauty is most readily expressed.
Modifications of a decidedly esthetic character are generally suggested to the primitive mind by some functional, constructive, or accidental feature which may with ease be turned in the new direction. In the vessel presented in Fig. 289—the work of Alaskan Indians—the margin is varied by altering the relations of the three marginal turns of the coil, producing a scalloped effect. This is without reference to use, is uncalled for in construction, and hence is, in all probability, the direct result of esthetic tendencies. Other and much more elaborate examples may be found in the basketry of almost all countries.
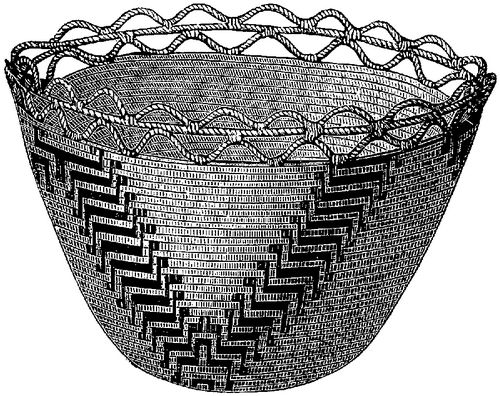
Fig. 289. Vessel with esthetic characters of form. Work of the Yakama—1/4.ToList
In the pursuit of this class of enrichment there is occasionally noticeable a tendency to overload the subject with extraneous details. This is not apt to occur, however, in the indigenous practice of an art, but comes more frequently from a loss of equilibrium or balance in motives or desires, caused by untoward exotic influence. When, through suggestions derived from contact with civilized art, the savage undertakes to secure all the grace and complexity observed in the works of more cultured peoples, he does so at the expense of construction and adaptability to use. An example of such work is presented in Fig. 290, a weak, useless, and wholly vicious piece of basketry. Other equally meretricious pieces represent goblets, bottles, and tea pots. They are the work of the Indians of the northwest coast and are executed in the neatest possible manner, bearing evidence of the existence of cultivated taste.
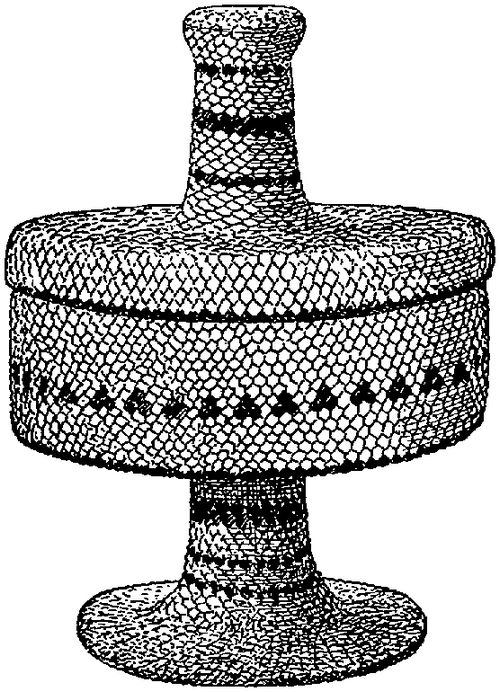
Fig. 290. Basket made under foreign influence, construction and use being sacrificed to fancied beauty—1/3.ToList
It appears from the preceding analyses that form in this art is not sufficiently sensitive to receive impressions readily from the delicate touch of esthetic fingers; besides, there are peculiar difficulties in the way of detecting traces of the presence and supervision of taste. The inherent morphologic forces of the art are strong and stubborn and tend to produce the precise classes of results that we, at this stage of culture, are inclined to attribute to esthetic influence. If, in the making of a vessel, the demands of use are fully satisfied, if construction is perfect of its kind, if materials are uniformly suitable, and if models are not absolutely bad, it follows that the result must necessarily possess in a high degree those very attributes that all agree are pleasing to the eye.
In a primitive water vessel function gives a full outline, as capacity is a prime consideration; convenience of use calls for a narrow neck and a conical base; construction and materials unite to impose certain limitations to curves and their combinations, from which the artist cannot readily free himself. Models furnished by nature, as they are usually graceful, do not interfere with the preceding agencies, and all these forces united tend to give symmetry, grace, and the unity that belongs to simplicity. Taste which is in a formative state can but fall in with these tendencies of the art, and must be led by them, and led in a measure corresponding to their persistency and universality. If the textile art had been the only one known to man, ideas of the esthetic in shape would have been in a great measure formed through that art. Natural forms would have had little to do with it except through models furnished directly to and utilized by the art, for the ideas of primitive men concentrate about that upon which their hands work and upon which their thoughts from necessity dwell with steady attention from generation to generation.